 Share this!
Share this!Undeniably, youth play a crucial role in the action plans to limit the spread of the COVID-19 and its adverse impact on public health, society and the economy at large. Young people are also among the most vulnerable groups who suffer from the pernicious consequences derived from this crisis.
Labour turmoils
The pandemic is admittedly making young people the main victims of labour market shocks. According to Eurostat, in April 2020 while the general unemployment rate increased by 0.2%, from 6.4% to 6.6%, the youth unemployment rate increased by 0.8%, from 14.6% to 15.4%. In OECD countries, the unemployment rate rose faster among women and young people aged 15 to 24 as reflected in the graphic below:
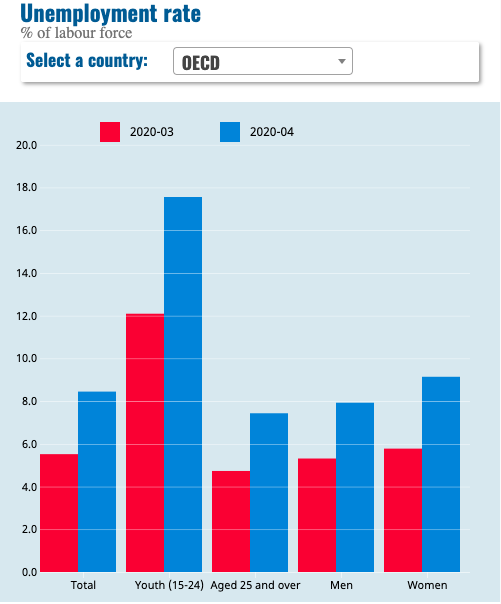
Over 1 in 6 young people worldwide have stopped working since the start of the crisis, according to ILO. This disproportionate escalation of youth unemployment can only be attributed to the fact that young people are overrepresented in informal employment –77% of employed young people hold informal jobs worldwide [1]– and in job sectors most at risk (ex. tourism, retail trades, personal services) from the COVID-19 shutdown. In light of these negative developments, the quality of jobs for young people will severely deteriorate and temporary contracts will become more prominent.
Socio-economic gaps
As unemployment grows, the socio-economic gaps between young people, and across generations, become more profound amid the economic and health crisis. Access to social protection is one of the major concerns and significantly varies depending on a person’s background (including age). As many welfare programmes are linked to formal employment, that leaves many young people unprotected, especially young women, and more exposed to health-related hazards [2].
In Education, the COVID-19 pandemic is altering learning, compromising nutrition and increasing the drop-out rates as a result of the nationwide closures of educational institutions. In this context, disadvantaged children and youth who have fewer economic or educational opportunities outside of school, limited access to e-learning tools and depend on free or discounted school meals are at risk of falling further behind [3].
Not to mention the young migrants and refugees. Given that 70% of all international migrants are below 30 years of age globally [4], epidemics like the COVID-19 will hit this concrete population group the hardest. What is more, the pandemic will limit even more their access to healthcare and livelihood provisions while exacerbating the social stigmas towards any minority group.
Building mental resilience
The COVID-19 outbreak has triggered detrimental effects on the wellness and mental health of children and young people. The short-term quarantine measures and social distancing turn out to have greater psychological implications for the young population and contribute to exacerbating other household and individual circumstances: personal safety, prospects of job and income losses, medical conditions in the household, social connectedness or trust in other people and in institutions [5].
According to an OECD survey, more than half of young people express great concerns about their mental health. This requires immediate policy responses and long-term solutions to mitigate harm and proactively improve systems of support for young people and children. These measures may include: providing online resources; advice to general practitioners and youth workers; inclusive telemedicine consultations; and, overall, reinforcing resources for mental health services in the aftermath of the pandemic.
The WHO or Voices of Youth have published a compilation of resources such as guidance documents and Q&As in the area of COVID-19 & youth mental health. Furthermore, initiatives such as the Global survey on youth rights and COVID-19, a joint effort of the Global Initiative on Decent Jobs for Youth (DJY) and its partners, will shed further light, among various areas, on the psychological implications of COVID-19 for young individuals.
A call for intergenerational solidarity!
It is more imperative than ever that every administration level across Europe and beyond include young people in the recovery strategies and cooperates with every economic and social player to safeguard their rights and wellbeing. The Sustainable Development Goals are paramount in accelerating a vigorous response to overcome the epidemic as well as build resilience and “social immunity” that the world needs to prevent the next pandemic.
References
[1] UN DESA, World Economic Situation and Prospects, April 2019 briefing, no 123. [2] Special issue on COVID-19 and Youth (27 March 2020). Programme on Youth Unit, Division for Inclusive Social Development (DISD), Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA), United Nations. [3] UNESCO ”COVID-19 Educational Disruption and Response”: https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/coronavirus-schoolclosures [4] 2019 International Migration and Displacement Trends and Policies Report to the G20: https://www.oecd.org/migration/mig/G20-migrationand-displacement-trends-and-policies-report-2019.pdf [5] “The impact of COVID-19 on children and young people”. March 2020 The Children’s Society – United Kingdom. Policy and Research team.Photo credits: Mathias Jensen on Unsplash
